Hellman Key is a cryptographic key generated as part of the Diffie-Hellman key exchange protocol. This protocol, invented in the 1970s by Whitfield Diffie and Martin Hellman, allows two parties to create a shared secret over an insecure channel—without ever sending the secret itself. In other words, it’s the digital handshake that lets your device and a website agree on a secret code, even if hackers are listening in.
Why does this matter? Because every time you see that little padlock in your browser, or use a secure messaging app, there’s a good chance a Hellman key is working behind the scenes to keep your data private.
The Origins: Whitfield Diffie, Martin Hellman, and the Birth of Modern Cryptography
Before the 1970s, secure communication required both parties to share a secret key in advance—a logistical nightmare for global networks. Enter Whitfield Diffie and Martin Hellman, who published their groundbreaking paper in 1976. Their idea? Use complex math (modular exponentiation) to let two people create a shared secret, even if someone is eavesdropping.
This was the birth of public-key cryptography, and the Diffie-Hellman key exchange became the gold standard for secure digital communication.
How Does the Hellman Key Exchange Work?
Let’s break it down in simple terms:
- Agree on Public Parameters: Both parties agree on a large prime number (p) and a base (g). These are called DH values and are often standardized for security.
- Generate Private Keys: Each party picks a secret number (their private key).
- Compute Public Keys: Each party computes their public key using the formula:
Public Key = g^private_key mod p - Exchange Public Keys: They swap public keys over the insecure channel.
- Compute Shared Secret: Each party uses their own private key and the other’s public key to compute the shared secret:
Shared Secret = (Other’s Public Key)^private_key mod p
The magic? Both parties end up with the same shared secret, but an eavesdropper can’t figure it out without solving a nearly impossible math problem.
DH Values and DH Groups: The Building Blocks
You’ll often hear about DH values and DH group when discussing Hellman keys. Here’s what they mean:
- DH Values: The prime number (p) and base (g) used in the calculations. These must be large and carefully chosen to prevent attacks.
- DH Group: A set of standardized DH values, often defined by organizations like IETF. Common groups include Group 2 (1024-bit), Group 14 (2048-bit), and even larger ones for extra security.
Using well-known Diffie Hellman groups ensures that everyone is using safe, vetted parameters—crucial for modern cryptography.
Real-World Example: Hellman Key in Action
A network engineer recently shared,
“We had to upgrade our VPNs to use stronger DH groups after a security audit. Switching to a 4096-bit Diffie Hellman group made our connections much more secure, and our clients noticed faster, safer logins.”
This is a perfect example of how the right Hellman key and DH values can make a real difference in everyday security.
Why Are Diffie Hellman Groups So Important?
Not all DH groups are created equal. As computers get faster, older groups (like 1024-bit) become vulnerable to brute-force attacks. In 2025, security experts recommend using at least 2048-bit or 3072-bit groups for sensitive data.
Pro tip: Always check your VPN, SSH, or web server settings to ensure you’re using strong Diffie Hellman groups.
The Math Behind the Magic: Why Is the Hellman Key Secure?
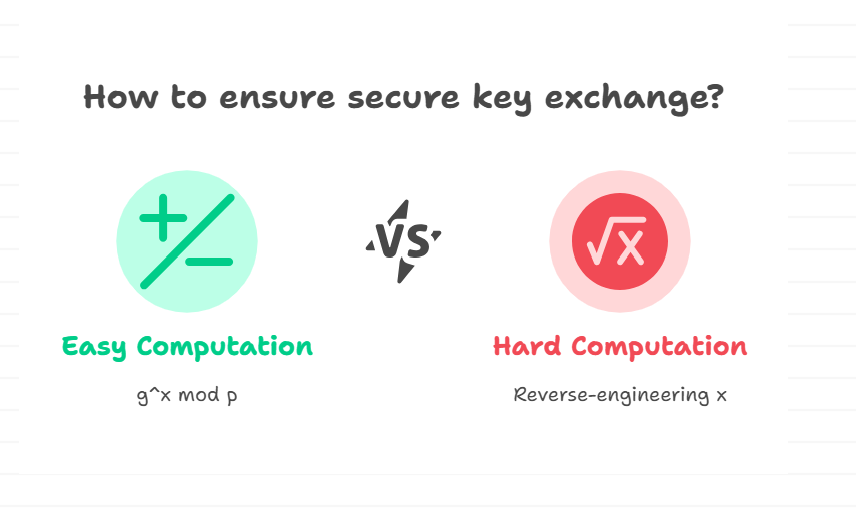
The security of the Hellman key exchange relies on the difficulty of the discrete logarithm problem. In simple terms, it’s easy to compute g^x mod p, but almost impossible to reverse-engineer x from the result—especially when p is a huge prime number.
Risks and Challenges: Is the Hellman Key Still Safe in 2025?
While the Hellman key exchange is still widely used, it’s not invincible. Here are some risks to watch for:
- Weak DH Values: Using small or poorly chosen primes can make the system vulnerable.
- Logjam Attack: A well-known attack that exploits weak DH groups.
- Quantum Computing: Future quantum computers could break current DH security, but post-quantum algorithms are being developed.
Best practice: Always use strong, up-to-date DH groups and stay informed about new cryptographic standards.
Hellman Key vs Other Key Exchange Methods
How does the Hellman key compare to other methods?
- RSA: Another popular key exchange, but slower and less secure against certain attacks.
- Elliptic Curve Diffie-Hellman (ECDH): Uses elliptic curves for even stronger security with smaller keys—popular in mobile and IoT devices.
- Post-Quantum Algorithms: New methods designed to resist quantum attacks, still being standardized in 2025.
For most applications, the classic Hellman key (with strong DH values) remains a solid choice.
How to Implement Hellman Key Exchange in 2025
If you’re a developer or IT pro, implementing Hellman key exchange is easier than ever. Most modern libraries (OpenSSL, Bouncy Castle, etc.) support secure DH groups out of the box.
Steps:
- Choose a strong DH group (2048-bit or higher).
- Use a reputable cryptographic library.
- Regularly update your software to patch vulnerabilities.
- Monitor for new standards, especially as quantum computing advances.
Whitfield Diffie: The Man Behind the Math
No discussion of the Hellman key is complete without mentioning Whitfield Diffie. Along with Martin Hellman, he revolutionized cryptography and laid the groundwork for everything from secure web browsing to encrypted messaging. Their work earned them the Turing Award and a place in cybersecurity history.
Diffie Hellman Groups: What’s New in 2025?
In 2025, the cryptographic community continues to refine and expand Diffie Hellman groups. New groups are being proposed to resist quantum attacks, and more organizations are moving to larger key sizes for extra safety.
Tip: Always check your software’s documentation to see which DH groups are supported and recommended.
Pros and Cons of the Hellman Key Exchange
Pros
- No Pre-Shared Secret Needed: Securely create a shared key over an insecure channel.
- Widely Supported: Used in VPNs, HTTPS, SSH, and more.
- Strong Security (with proper DH values): Resistant to most classical attacks.
Cons
- Vulnerable to Weak Parameters: Poor DH values can be exploited.
- No Authentication: By itself, doesn’t verify the identity of the other party (can be combined with digital signatures).
- Quantum Threat: May be broken by future quantum computers.
Hellman Key in Everyday Life: Where You’ll Find It
You might not realize it, but the Hellman key exchange is everywhere:
- Web Browsing: Every time you see HTTPS, there’s a good chance DH is involved.
- VPNs: Secure tunnels for remote work and privacy.
- Messaging Apps: End-to-end encryption for private chats.
- IoT Devices: Secure communication between smart gadgets.
How to Check Your DH Group and Values
Want to see which DH group your server or VPN is using? Here’s how:
- OpenSSL:
openssl s_client -connect yoursite.com:443 -cipher 'DHE' - VPN Logs:
Check your VPN client’s connection logs for DH group info. - SSH:
Use verbose mode (ssh -vvv) to see key exchange details.
If you see a group smaller than 2048 bits, it’s time to upgrade!
Real-World Example: Upgrading to Stronger DH Groups
A security consultant shared,
“After a penetration test, we found our web server was using a 1024-bit DH group. We upgraded to 3072-bit, and our security rating jumped from a C to an A+ overnight.”
This simple change can make a huge difference in your organization’s security posture.
FAQs
Q. What is a Hellman key used for?
A. Hellman key is used to securely generate a shared secret between two parties, enabling encrypted communication over an insecure network.
Q. What are DH values and why are they important?
A. DH values are the prime number and base used in the Diffie-Hellman exchange. Strong, standardized DH values are crucial for preventing attacks.
Q. Who is Whitfield Diffie?
A. Whitfield Diffie is a pioneering cryptographer who co-invented the Diffie-Hellman key exchange, revolutionizing secure digital communication.
Q. What are Diffie Hellman groups?
A. Diffie Hellman groups are standardized sets of DH values (prime and base) used to ensure secure and interoperable key exchanges.
The Future: Post-Quantum Cryptography and the Hellman Key
As quantum computing advances, the cryptographic community is preparing for a world where current DH groups may no longer be safe. Post-quantum algorithms are being developed and tested, but for now, strong DH groups remain a cornerstone of secure communication.
Risks and Best Practices for Using Hellman Keys in 2025
- Always use strong, up-to-date DH groups.
- Regularly audit your systems for weak parameters.
- Combine DH with authentication (like digital signatures) for extra security.
- Stay informed about quantum-safe cryptography.
Final Thoughts
In 2025, the Hellman key is as vital as ever. It’s the invisible shield protecting your data, your privacy, and your digital life. Whether you’re a developer, a business owner, or just someone who values security, understanding the basics of DH values, DH groups, and the legacy of Whitfield Diffie can help you make smarter, safer choices online.
CLICK HERE FOR MORE BLOG POSTS
“In a world of instant takes and AI-generated noise, John Authers writes like a human. His words carry weight—not just from knowledge, but from care. Readers don’t come to him for headlines; they come for meaning. He doesn’t just explain what happened—he helps you understand why it matters. That’s what sets him apart.”

