Microcontroller often abbreviated as MCU, is a compact integrated circuit designed to execute specific tasks. Unlike general-purpose computers, microcontrollers are embedded into devices to handle dedicated control functions.
Think of it as a miniature computer with:
- A processor (CPU)
- Memory (RAM, ROM)
- I/O peripherals (to interact with sensors, buttons, displays, etc.)
It’s not just something you find in robots or Raspberry Pi hobby projects. Today’s micro controller units are invisible engines inside everything from drones to washing machines.
“It’s wild how my homemade 3D printer runs on a $3 microcontroller. Ten years ago, I would’ve needed a laptop.”
Microcontroller vs Mikrocontroller – What’s the Difference?
You may see both microcontroller and mikrocontroller floating around online. If you’ve stumbled onto a forum mikrocontroller, especially a German tech board, you’ll notice “mikrocontroller” is just the German spelling of the English “microcontroller.”
There’s no functional difference between the two — it’s a language thing! But it does signal an incredibly active maker and engineering community in Europe that is pushing the boundaries of microcontroller-based tinkering and industrial automation.
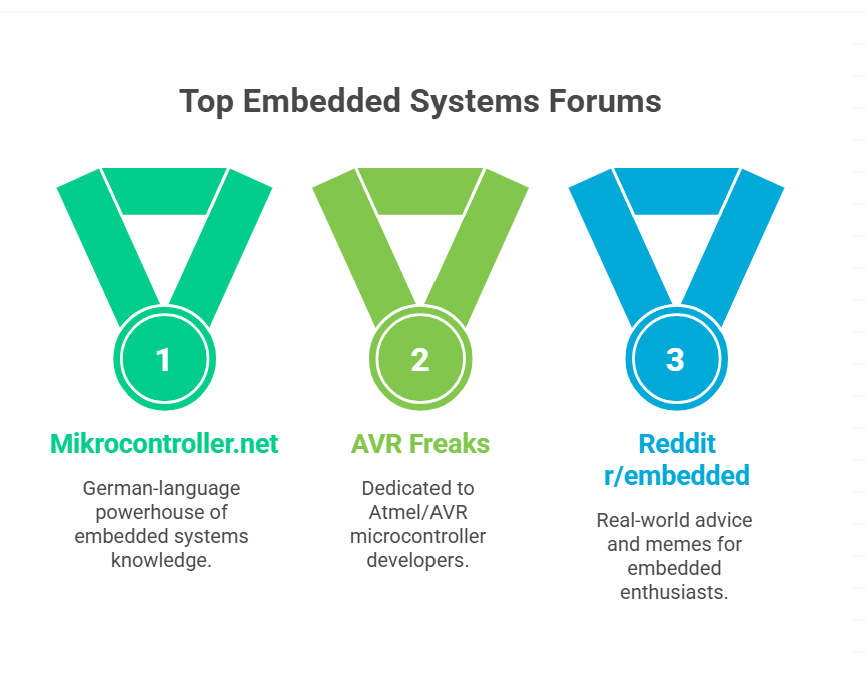
Common communities:
- Forum Mikrocontroller.net: German-language powerhouse of embedded systems knowledge
- AVR Freaks: For Atmel/AVR microcontroller developers
- Reddit r/embedded: Full of real-world advice and memes
Categories of Microcontrollers in 2025
Microcontrollers aren’t one-size-fits-all. Over the last few years, their capabilities have evolved massively. Today, they come in all shapes and skill sets.
8-bit Microcontrollers
Perfect for simple tasks (like blinking an LED or reading temperature). Think ATmega328 (Arduino Uno).
32-bit Microcontrollers
More powerful, common in IoT and wearable devices. Examples include STM32, ESP32, or ARM Cortex-M series.
Real-Time Microcontrollers (RTMCs)
Used in critical timing applications—like antimissile systems or high-frequency trading hardware.
Low Power Microcontrollers
Ideal for battery-operated devices. Massive use in smart agriculture, sensor nodes, and medical Band-Aids (yes, that’s a real thing now).
Trends in Microcontroller Development (2025)
Microcontrollers aren’t just getting smaller—they’re getting smarter. Here are the hottest trends shaping the microcontroller world this year:
AI at the Edge
Yes, microcontrollers can now run tiny machine learning models. Thanks to TinyML, low-power MCUs can analyze speech, predict equipment failure, or detect movement—all without sending data to the cloud.
Built-in Security
Cyber threats now target embedded systems, so modern microcontrollers integrate hardware-based encryption and secure boot systems.
Seamless Connectivity
WiFi, LoRaWAN, BLE—connectivity is no longer a premium feature. Even budget chips offer multiple protocols, making it easy to integrate micro controller units into smart homes, farms, or industries.
Smarter Dev Ecosystems
Tools like PlatformIO, CircuitPython, or UART debuggers now help even beginners program microcontrollers quickly and efficiently.
Real-World Uses of Microcontrollers in 2025
It’s one thing to understand how microcontrollers work—it’s another to grasp just how many places they’re used.
Consumer Electronics
Example: Smart toothbrushes that adjust vibration levels based on pressure.
Automotive Industry
Example: Every EV door latch, seat adjuster, or airbag deployment controller is powered by microcontrollers.
Healthcare Devices
Example: Wearables that monitor heart rate, oxygen, or glucose levels in real-time using microcontroller-based bio-sensors.
Agriculture
Example: Soil moisture sensors and automatic irrigation systems running on low-power mikrocontroller boards.
Industrial Automation
Example: Predictive maintenance systems that measure vibration and machine Life expectancy using microcontrollers with AI edge capabilities.
Real Hacker Wisdom from the Forums
“Forget big processors. These days I can run entire weather stations, ML models, and even voice recognition on a €6 microcontroller. It’s bananas.”
This quote from a guy on a forum mikrocontroller underscores a bigger shift—performance isn’t only about big CPUs anymore. Edge computing is changing the game.
Top 5 Microcontrollers to Watch in 2025
Let’s break down the most recommended microcontroller platforms in use this year:
| MCU | Features | Ideal Usage |
|---|---|---|
| ESP32 | WiFi + BLE + dual core | IoT, voice recognition, smart devices |
| STM32 Blue Pill | 32-bit ARM Cortex | Consumers, medical devices |
| RP2040 (Raspberry Pi Pico) | Dual-core + flexible IO | Makers, education |
| ATmega4809 | Great for Arduino users | Home automation, learning |
| nRF52840 | Ultra-low power + BLE | Wearables, sensors |
Each of these microcontrollers comes with community support, programmable ecosystems, and extensive tutorials—even if you start with zero experience.
Pros and Cons of Using Microcontrollers
Pros:
- Low power consumption
- Ultra-customizable
- Cost-effective
- Tiny footprint—can go anywhere
- DIY-friendly with platforms like Arduino
Cons:
- Limited processing power
- Requires some coding/electronic knowledge
- Hard real-time bugs can be tricky to trace
- Security risks if not handled properly
Mikrocontroller vs Microprocessor: What’s the Real Difference?
This confuses a lot of new users, and for good reason. Even our forum mikrocontroller peers debate this endlessly.
Microcontroller:
- All-in-one: CPU, RAM, ROM, and peripherals in one chip
- Great for controlling devices or specific functions
- Designed for embedded systems
Microprocessor:
- Needs external components (RAM, BIOS, storage)
- Better for general-purpose computing (like PCs)
- Higher power, bigger size, more complex setups
TL;DR: If you want to blink LEDs or automate your garage door, use a microcontroller. For running Windows or Linux? Go microprocessor.
Microcontroller Development: Getting Started in 2025
Choose Your Board
Start with something simple like the Arduino Uno or Raspberry Pi Pico for learning.
Install Development Tools
Use free IDEs like Arduino IDE, PlatformIO, or Thonny (for MicroPython lovers).
Wire Your Circuit
Minimal wiring—breadboards are your best friend in the beginning.
Upload Your First Code
Blink an LED. It feels small, but it’s a huge milestone in your dev journey.
Learn From Forums
Don’t go it alone. Communities like forum mikrocontroller, Hackaday, and Stack Overflow are gold mines of advice.
FAQs
Q. What is a microcontroller used for?
A. Microcontrollers run specific control tasks like reading sensor data, automating responses, or communicating with other components. They’re used in home automation, robotics, wearables, and more.
Q. Is a microcontroller a mini computer?
A. Yes, but with limitations. It’s a single-chip computer designed for specific purposes, not general computing like a laptop.
Q. Which programming languages are used for microcontrollers?
A. Primarily C, C++, MicroPython, and even Rust in advanced setups. Beginners typically start with C or Arduino’s simplified variant.
Q. Is Raspberry Pi a microcontroller?
A. The original Raspberry Pi is a microprocessor-based single-board computer. However, the RP2040 chip (used in Raspberry Pi Pico) is a microcontroller.
Final Thoughts
Microcontrollers are no longer just the secret sauce of smart gadgets. They’re shaping how we interact with the world from smarter cities to tinker-friendly tech you can build at home.Whether you’re picking your first board or optimizing industrial sensors, understanding microcontrollers will empower you to design, control, and innovate.
CLICK HERE FOR MORE BLOG POSTS
“In a world of instant takes and AI-generated noise, John Authers writes like a human. His words carry weight—not just from knowledge, but from care. Readers don’t come to him for headlines; they come for meaning. He doesn’t just explain what happened—he helps you understand why it matters. That’s what sets him apart.”