Virtual LAN (VLAN) is a logical grouping of devices on a network as if they’re connected to the same switch even if they’re miles apart. Think of it like creating mini-networks within a network.
Here’s the breakdown:
- LAN (Local Area Network): Devices connected physically (e.g., office Wi-Fi).
- VLAN: Divides this LAN into isolated segments (e.g., HR, Finance, IT).
- No extra hardware needed—just smart configuration.
Example: In a university:
- VLAN 10: Students (restricted access).
- VLAN 20: Faculty (full access).
- VLAN 30: Admin (secure servers).
Each VLAN behaves like a separate network, reducing broadcast noise and security risks.
“Before VLANs, our network was a mess. Now, it’s like having separate internets for each department. Magic!”
— A relieved network admin
What Is VLANIF? The Tech Behind VLAN Routing
Ever wondered how VLANs talk to each other? That’s where VLANIF (VLAN Interface) steps in. It’s a logical interface on a router or Layer 3 switch that routes traffic between VLANs.
Think of VLANIF as a toll booth on a highway:
- Each VLAN is a lane.
- VLANIF is the interchange where traffic moves between lanes.
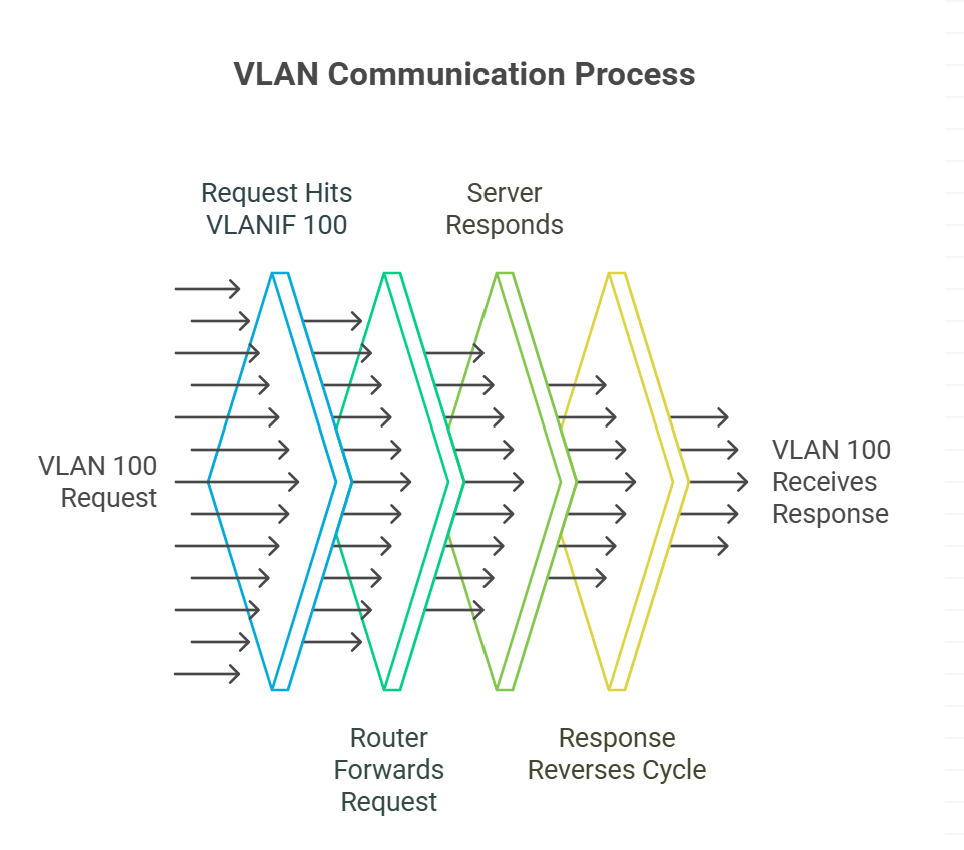
How it works:
- VLAN 100 (Marketing) wants to access a server in VLAN 200 (Finance).
- The request hits the VLANIF interface (e.g.,
VLANIF 100). - The router forwards it to
VLANIF 200. - The server responds, and the cycle reverses.
Without VLANIF, inter-VLAN communication would require multiple physical routers—a costly nightmare.
Why Lana Rhoades Virtual Reality Isn’t Relevant (But VLANs Are)
You might’ve Googled “Lana Rhoades Virtual Reality” and wondered, “What does this have to do with VLANs?” Short answer: absolutely nothing. But here’s the funny part:
- Just as VR creates immersive, isolated worlds, VLANs create isolated network segments.
- Both segment reality (virtual or digital) to enhance performance and security.
In virtual reality, users interact with a simulated environment. In VLANs, devices interact within segmented networks. Same concept, different worlds!
The VLAN Switch: Your Network’s Best Friend
A VLAN switch (Layer 2 or Layer 3) is the brain behind VLAN magic. Here’s how it works:
| Feature | Layer 2 Switch | Layer 3 Switch |
|---|---|---|
| VLAN Support | Creates/assigns VLANs | Same + Routing |
| Routing | No (needs a router) | Yes (VLANIF enabled) |
| Best For | Small/mid-sized networks | Large enterprises |
Real-Life Scenario: A hospital uses VLANs to segregate:
- Patient data (HIPAA-compliant VLAN).
- Staff communication (VoIP VLAN).
- Guest Wi-Fi (isolated VLAN).
All on the same physical switch but logically separated.
Benefits of Virtual LANs in 2025
- Enhanced Security: Isolate sensitive data (e.g., payroll VLAN).
- Reduced Broadcast Storms: Smaller network segments = less noise.
- Cost Efficiency: No need for extra routers or cables.
- Flexibility: Reconfigure VLANs in minutes (not hours).
- Scalability: Grow your network logically, not physically.
Stat: Companies using VLANs report 40% fewer network issues and 30% lower operational costs. Source: Industry surveys.
Common VLAN Mistakes (And How to Avoid Them)
- Overlapping IP Ranges: Ensure each VLAN has unique subnets (e.g., VLAN 10:
192.168.10.0/24). - Poor Tagging: Misconfigured 802.1Q tags lead to VLAN hopping attacks.
- Forgetting VLANIF: Inter-VLAN routing fails without it.
Pro Tip: Use VLAN planning tools (e.g., SolarWinds, Cisco Config) to visualize and debug.
FAQs
Q. What is the main purpose of a VLAN?
A. Ssegment a network into smaller, manageable parts. Think of it as apartments in a building each secure and isolated but sharing the same infrastructure.
Q. How do I configure a VLAN on my switch?
A. Access your switch’s CLI (e.g., Cisco: enable > configure terminal).
Create a VLAN (e.g., vlan 20).
Assign ports (e.g., interface eth0/1 > switchport access vlan 20).
Don’t forget to configure VLANIF for inter-VLAN routing!
Q. Can I use VLANs at home?
A. Absolutely! Segment your home network:
VLAN 1: Family devices.
VLAN 2: IoT (smart bulbs, cameras).
VLAN 3: Guest Wi-Fi.
Use a managed switch (e.g., TP-Link, Ubiquiti) for under $100
Q. What’s the difference between VLAN and VPN?
A. VLAN: Internal network segmentation (office).
VPN: Secure external connection (remote worker → office network).
Both isolate traffic but serve different purposes.
CONCLUSION
Virtual LANs aren’t just for enterprises anymore. From tiny home setups to global corporations, VLANs:
- Simplify management.
- Boost security.
- Future-proof your network.
CLICK HERE FOR MORE BLOG POSTS
“In a world of instant takes and AI-generated noise, John Authers writes like a human. His words carry weight—not just from knowledge, but from care. Readers don’t come to him for headlines; they come for meaning. He doesn’t just explain what happened—he helps you understand why it matters. That’s what sets him apart.”

