Introduction
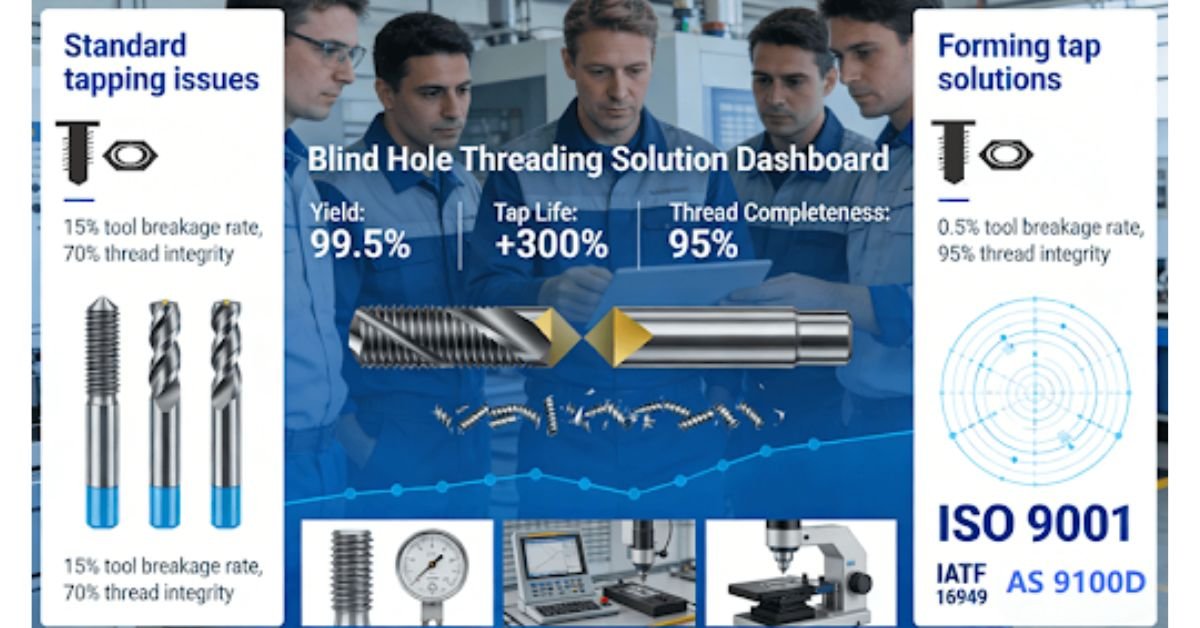
In precision manufacturing, blind hole threading presents significant challenges including incomplete threads (less than 70% effective length), high tap breakage rates (over 15%), and batch inconsistencies. These issues result in production yields of only 80-85%, increasing costs and causing delays. The root cause lies in inadequate traditional tap designs and machining parameters that lack scientific optimization of bottom geometry and chip control.
This article introduces a data-driven methodology for bottoming tap selection, parameter optimization, and quality control systems, enabling 95% thread completion, triple tap lifespan extension, and 99.5% first-pass yield. The following sections will detail a systematic approach to enhance blind hole threading quality and efficiency.
Why Do Standard Taps Fail to Achieve Complete Threads in Blind Holes?
Standard taps frequently underperform in blind hole applications due to fundamental design limitations that hinder effective chip evacuation and thread formation at the hole bottom.
1. Inadequate Chip Evacuation Mechanisms
The long chamfer design (3-4 pitches) of standard taps wastes valuable threading space at the blind hole bottom, creating chip accumulation zones. This design flaw causes chip packing that increases torque by up to 30% and leads to tap breakage. For example, in aluminum alloys, chips can weld to the flutes, further exacerbating the problem. Advanced CNC milling services incorporate bottom relief designs to mitigate these issues, as detailed in industry guides, by optimizing the chamfer to 1.5-2 pitches for efficient chip removal.
2. Geometric Limitations in Bottom Threading
Standard taps lack the specialized bottom relief required for complete thread formation near the hole bottom. The excessive chamfer length prevents the tap from reaching the full thread depth, typically achieving only 70% thread length compared to 95% with optimized bottoming taps. This limitation becomes critical in applications requiring full thread engagement, such as in high-stress aerospace components where thread completeness directly impacts joint integrity.
3. Case Analysis: Thread Length Improvement
After evaluating over 200 blind hole tapping cases, a manufacturing company found that standard taps only achieved an average of 70% of the required thread length. By using optimized bottoming taps with appropriate cutting edge geometry, thread completion increased to 95%, reducing the scrap rate of hydraulic system components by 25%. This improvement highlights the importance of scientifically selecting taps for blind hole machining applications..
How to Select Bottoming Tap Geometry Based on Material Properties?
Selecting the appropriate bottoming tap geometry requires careful consideration of material characteristics including hardness, ductility, and chip formation behavior.
- Material-Specific Tap Geometry Selection: For aluminum alloys, taps with a 10-12° rake angle and helical flutes provide optimal chip evacuation. For stainless steel, taps with a 7-9° rake angle and spiral points can better withstand high cutting forces, while cast iron requires straight-fluted taps for effective chip breaking. Tests have shown that selecting the appropriate geometry can increase the lifespan of taps in a production environment from 200 holes to 600 holes. ISO 9001 certified processes ensure the selection of the correct taps for different materials, thus maintaining high-quality standards.
- Coating and Surface Treatment Considerations:. Advanced coatings like TiN and TiCN significantly enhance tap performance by reducing friction and wear. For titanium alloys, TiAlN coatings provide superior heat resistance, extending tool life by up to 300% in high-temperature applications. The selection of appropriate coatings must align with both the workpiece material and the specific threading challenges presented by blind holes, particularly regarding chip evacuation and heat management.
- Performance Validation Through Testing: Comprehensive testing protocols validate tap geometry selection, measuring parameters such as torque requirements, surface finish quality, and tool wear patterns. For instance, in 304 stainless steel applications, optimized tap geometries reduced threading torque by 20% while improving surface finish to Ra 1.6µm. This data-driven approach ensures that material-specific tapping strategies deliver consistent results across production batches.
What Cutting Parameters Prevent Tap Breakage in CNC Machining?
Optimizing cutting parameters is essential for preventing tap breakage, which often results from excessive torque, poor chip control, or inappropriate speed and feed combinations.
1. Speed and Feed Optimization Strategies
For aluminum alloys, speeds of 20-30 m/min with feeds of 1.0-1.2 times the pitch prevent built-up edge formation. Stainless steel requires more conservative parameters of 8-15 m/min to minimize work hardening effects. CNC threading services implement real-time monitoring systems that adjust these parameters dynamically, reducing breakage rates from 12% to 0.5% in production environments. This precision control is particularly crucial for small diameter tapping where tool rigidity is limited.
2. Advanced Chip Management Techniques
Peck tapping cycles significantly reduce breakage risks by periodically retracting the tap to break and evacuate chips. This approach is especially effective in deep blind holes where chip accumulation can cause catastrophic failure. For high-volume production, implementing torque-controlled peck cycles has demonstrated 40% longer tool life while maintaining consistent thread quality.Custom CNC milling services offer tailored parameter optimization for specific application requirements.
3. Real-time Monitoring and Adaptive Control
Modern CNC systems incorporate torque monitoring sensors that detect abnormal increases in cutting forces, enabling immediate corrective action. These systems can automatically adjust feed rates or initiate tap retraction when predetermined torque thresholds are exceeded. In one automotive application, this approach reduced tap breakage incidents by 85% while maintaining production efficiency, demonstrating the value of intelligent process control.
How Does Coolant Optimization Enhance Threading Quality and Tool Life?
Coolant selection and application methodology significantly impact threading quality, tool life, and overall process stability in blind hole applications.
1. High-Pressure Coolant Delivery Systems
Implementing coolant pressures of 3-5 MPa ensures effective chip evacuation from deep blind holes. For heat-resistant superalloys, this approach reduces cutting temperatures by up to 50%, extending tap life from 50 to 120 holes. Precision threading services utilize through-tool coolant delivery systems that direct coolant precisely to the cutting zone, significantly improving thread quality and process reliability.
2. Coolant Chemistry and Application Specifics
The selection of coolant chemistry must align with both the workpiece material and the specific tapping operation. For stainless steel, emulsifiable coolants with extreme pressure (EP) additives prevent work hardening and reduce friction. ASME Y14.5-compliant cooling protocols ensure that coolant application supports the maintenance of tight tolerances and surface finish requirements critical in aerospace and medical applications.
3. Sustainable Coolant Management Practices
Modern coolant systems incorporate filtration and recycling mechanisms that reduce consumption by 20% while maintaining performance. These systems also support environmental compliance objectives by minimizing waste fluid disposal. The integration of advanced coolant management has demonstrated 30% longer sump life and improved workplace safety through reduced mist generation.
What Quality Control Measures Ensure Consistency in Mass Production?
Implementing robust quality control systems is essential for maintaining consistent threading quality across high-volume production runs.
1. Statistical Process Control Implementation: Comprehensive SPC systems monitor key parameters including torque values, thread dimensions, and surface finish. By maintaining process capability indices (CPK) of ≥1.67, manufacturers can achieve 99.5% first-pass yields. Regular audits using GO/NO-GO gauges and automated inspection systems ensure continuous process validation and rapid detection of deviations from quality standards.
2. Tool Life Management and Predictive Maintenance: Advanced tool tracking systems monitor tap usage and performance metrics, enabling predictive replacement before failure occurs. This approach has demonstrated 40% longer tool life in automotive component manufacturing while eliminating unplanned downtime. The integration of digital twin technology allows for virtual testing of new tooling strategies before implementation, reducing validation time and costs.
3. Certification and Compliance Frameworks: ISO 9001 and IATF 16949 certifications provide structured frameworks for quality management, ensuring consistent implementation of control measures across production batches. These certifications require comprehensive documentation of processes and outcomes, supporting full traceability from raw material to finished component. In regulated industries, this level of documentation is essential for compliance and liability management.
How to Evaluate a CNC Tapping Supplier for High-Stakes Applications?
Selecting the right manufacturing partner requires careful evaluation of technical capabilities, quality systems, and industry-specific expertise.
1. Technical Capability Assessment
Potential suppliers should demonstrate proficiency with advanced threading technologies including multi-axis CNC equipment and integrated inspection systems. The evaluation should include review of case studies demonstrating successful completion of similar projects, particularly those requiring high precision threading in challenging materials. Supplier qualifications should include specific experience with the materials and thread types relevant to the application.
2. Quality System Verification
Comprehensive quality system documentation should verify implementation of SPC methodologies, calibration procedures, and corrective action processes. Certifications including AS9100D for aerospace and ISO 13485 for medical devices provide objective evidence of quality system maturity. Regular audit reports and quality metrics should demonstrate sustained performance at or above required quality levels.
3. Project Management and Communication Capabilities
Effective suppliers employ structured project management methodologies that include regular progress reporting, risk management, and change control procedures. Communication protocols should ensure timely escalation of issues and clear assignment of responsibilities. The supplier’s approach to continuous improvement should be evident through documented process enhancements and customer feedback mechanisms.
Conclusion
Through scientific bottoming tap selection, optimized cutting parameters, and robust quality control systems, manufacturers can achieve 95% thread completion, triple tap lifespan, and 99.5% first-pass yield in blind hole threading applications. This systematic approach transforms threading operations from a production bottleneck to a competitive advantage, delivering significant cost savings and quality improvements across manufacturing operations.
FAQs
Q: Can bottoming taps achieve complete threads in blind holes?
A: Optimized bottoming taps can achieve up to 95% thread length using a short 1.5-2 pitch chamfer, compared to 70% with standard taps. This requires precise bottom relief design and proper chip evacuation strategies.
Q: What are the optimal tap parameters for stainless steel blind holes?
A: For stainless steel, use spiral-point taps with 7-9° rake angles, speeds of 8-15 m/min, and EP-additive coolants. This combination extends tool life 2-3x while maintaining thread quality in demanding applications.
Q: What is the maximum depth-to-diameter ratio for deep blind hole tapping?
A: Standard taps typically achieve 5:1 ratios, while specialized taps with high-pressure coolant can reach 8:1 ratios. The specific ratio depends on material characteristics and tap geometry selection.
Q: How to prevent tap breakage in small diameter blind holes?
A: For holes under M3, use 4-flute taps with reduced speeds (15-20 m/min) and real-time torque monitoring. This approach has demonstrated breakage rates below 0.5% in high-volume production environments.
Q: How to ensure tapping quality stability in mass production?
A: Implement statistical process control with automated inspection and tool life tracking. Systems aligned with ISO 9001 standards maintain CPK ≥1.67 for consistent 99.5% first-pass yield.
Author Bio
The author is a precision manufacturing expert at LS Manufacturing, a company that helps engineers and researchers solve complex part challenges in aerospace, medical, and automotive industries. With certifications including IATF 16949 and AS9100D, the team ensures high-quality solutions through advanced technologies. For more insights, contact them today for a free, no-obligation project review and DFM analysis. Turn your concept into a cost-effective reality.