Client access server (CAS) acts as the gateway between your devices (laptops, phones, tablets) and the backend servers (email, databases, apps). Think of it as the receptionist of your digital office—directing requests, authenticating users, and ensuring smooth data flow.
In Microsoft Exchange environments (a popular email server), the CAS role is critical. It handles:
- Outlook Web Access (OWA): Web-based email.
- ActiveSync: Syncing emails on your mobile.
- MAPI (Messaging API): Desktop Outlook connections.
Without a CAS, your exchange client (e.g., Outlook) would be lost, unable to fetch emails or calendar events.
Real-Life Example: A mid-sized law firm struggled with slow email access during peak hours. After optimizing their client access server configuration (load balancing and caching), email load times dropped by 70%. Lawyers quipped: “Now our emails are faster than our billable hours.”
How Client Access Servers Work Behind the Scenes
Here’s a peek under the hood:
- Client Request: Your Outlook app asks for new emails.
- CAS Authentication: The client access server verifies your login (username/password).
- Proxying Requests: CAS routes your request to the backend Mailbox Server.
- Data Retrieval: The Mailbox Server fetches emails and sends them back via CAS.
- Delivery: Emails land in your inbox, seamlessly.
It’s like ordering food at a restaurant:
- You (client) give the order.
- The waiter (CAS) takes it to the kitchen (Mailbox Server).
- The chef (backend) prepares your meal (data).
- The waiter delivers it back to you.
Client Exchange Group: Organizing Access Efficiently
In large organizations, managing individual client access servers can get chaotic. That’s where client exchange groups come in—logical groupings of CAS servers for load balancing and redundancy.
Think of it like a restaurant chain:
- Each outlet (CAS) serves customers (clients).
- If one outlet is busy, the next available one handles the load.
- If an outlet fails, others step in seamlessly.
Benefits of Client Exchange Groups:
- High Availability: No downtime even if a CAS crashes.
- Scalability: Add more CAS servers as your company grows.
- Load Balancing: Distribute traffic evenly (no overworked servers).
A client exchange group ensures your 10,000 employees don’t face email outages during a board meeting.
The Licensing Puzzle: Server Client Access License (CAL)
Here’s where most admins scratch their heads. Server Client Access Licenses (CALs) are permissions that allow users/devices to access Exchange services via the client access server.
Types of CALs:
- User CAL: One license per employee, regardless of devices used.
- Device CAL: One license per device (shared workstations, kiosks).
Example Scenario:
- Company A has 500 employees but only 300 workstations.
- User CALs cost: 500 licenses × $60 = $30,000.
- Device CALs cost: 300 licenses × $60 = $18,000.
Choose wisely! Miscalculating CALs can inflate your IT budget by tens of thousands.
Pro Tip: Microsoft 365 now bundles CALs with subscriptions. Upgrade to Exchange Online and save the licensing headache.
Features and Benefits of Client Access Servers in 2025
The client access server role has evolved. Here’s what’s new:
- Hybrid Deployments: Mix on-premises CAS with cloud Exchange (seamless migration).
- Enhanced Security: CAS now supports modern auth (OAuth 2.0) and MFA.
- Unified Messaging: Voicemail, emails, and faxes in one inbox.
- Mobile Optimization: Lightning-fast access for exchange clients on iOS/Android.
But with great power comes complexity. Misconfigured CAS settings can lead to:
- Slow email sync
- Authentication loops
- Data leaks (if not encrypted)
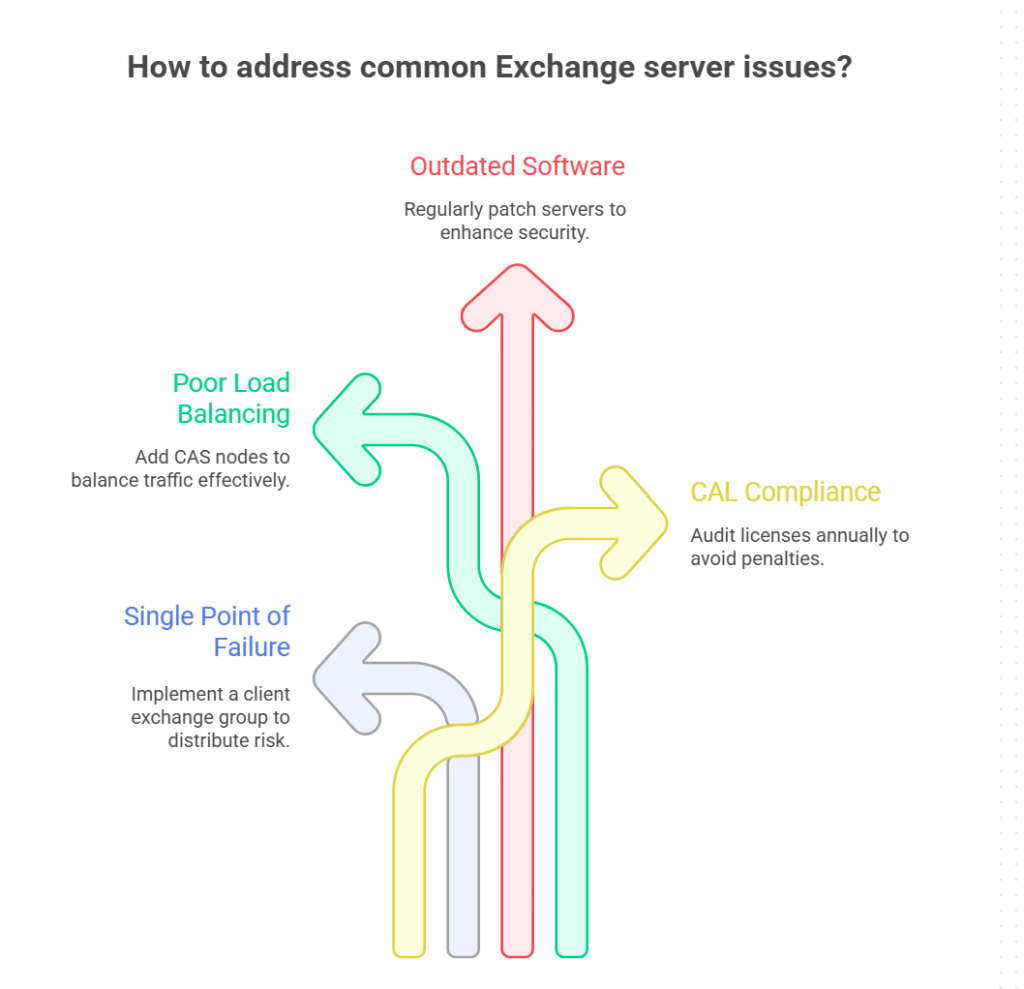
Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
- Single Point of Failure: Don’t rely on one CAS. Create a client exchange group.
- Poor Load Balancing: Monitor traffic; add CAS nodes as needed.
- Outdated Software: Regularly patch your Exchange servers (security vulnerabilities).
- Overlooking CAL Compliance: Audit licenses annually to avoid audits/fines.
A frustrated admin once tweeted: “Spent 3 days debugging Outlook slowness. Turns out, our CAS was overloaded. Load balancing 101, folks!”
Setting Up and Optimizing Your Client Access Server
Ready to roll up your sleeves? Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Install the CAS Role: Via Exchange Setup Wizard (GUI or PowerShell).
- Configure SSL Certificates: Encrypt client-server traffic.
- Enable Load Balancing: Distribute load across multiple CAS servers.
- Test Connectivity: Use tools like Test-OutlookConnectivity (Exchange cmdlet).
- Monitor Performance: Track CPU, RAM, and latency metrics.
PowerShell Snippet:
PowerShell# Add a new CAS to your Exchange group
New-ExchangeServer -Name "CAS-02" -Role ClientAccess
# Enable load balancing
Set-ClientAccessServer -Identity "CAS-02" -AutoDiscoverServiceInternalUri "https://mail.yourdomain.com/autodiscover/autodiscover.xml"
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: What’s the difference between a Client Access Server and a Mailbox Server?
A: A CAS handles client requests (Outlook, web, mobile), while the Mailbox Server stores emails, calendars, and data. Think of CAS as the lobby and Mailbox Server as the vault.
Q2: Do I need a separate CAS for every Exchange database?
A: No, one CAS can serve multiple Mailbox Databases. But for high availability, create a client exchange group with 2+ CAS servers.
Q3: Can I use a third-party load balancer with Exchange CAS?
A: Yes, but ensure it’s certified for Exchange (e.g., F5, Kemp). Misconfigured load balancers cause session timeouts.
Q4: How many CALs do I need for 1,000 employees?
A: It depends. If each uses 2+ devices, User CALs are cheaper ($60 × 1,000 = 60,000
(60,000).Forshareddevices(100workstations),∗∗DeviceCALs∗∗savemoney(60 × 100 = $6,000).
The Future of Client Access Servers: What’s Next?
- Cloud-First Architectures: More businesses migrate to Exchange Online (Microsoft 365).
- AI-Driven Monitoring: Predictive analytics detect CAS bottlenecks before they fail.
- Zero Trust Security: CAS enforces “verify every request” policies.
- 5G Integration: Faster mobile access for exchange clients worldwide.
The client access server isn’t just a tech role; it’s the backbone of modern workplaces.
Conclusion
Client access server isn’t a luxury; it’s a necessity. From client exchange groups to server client access licenses, every detail matters. Now that you’re armed with this knowledge, go forth and:
- Audit your current CAS setup.
- Optimize load balancing and security.
- Explore hybrid Exchange deployments for flexibility.
CLICK HERE FOR MORE BLOG POSTS
“In a world of instant takes and AI-generated noise, John Authers writes like a human. His words carry weight—not just from knowledge, but from care. Readers don’t come to him for headlines; they come for meaning. He doesn’t just explain what happened—he helps you understand why it matters. That’s what sets him apart.”


Great insights — thank you for the clarity!